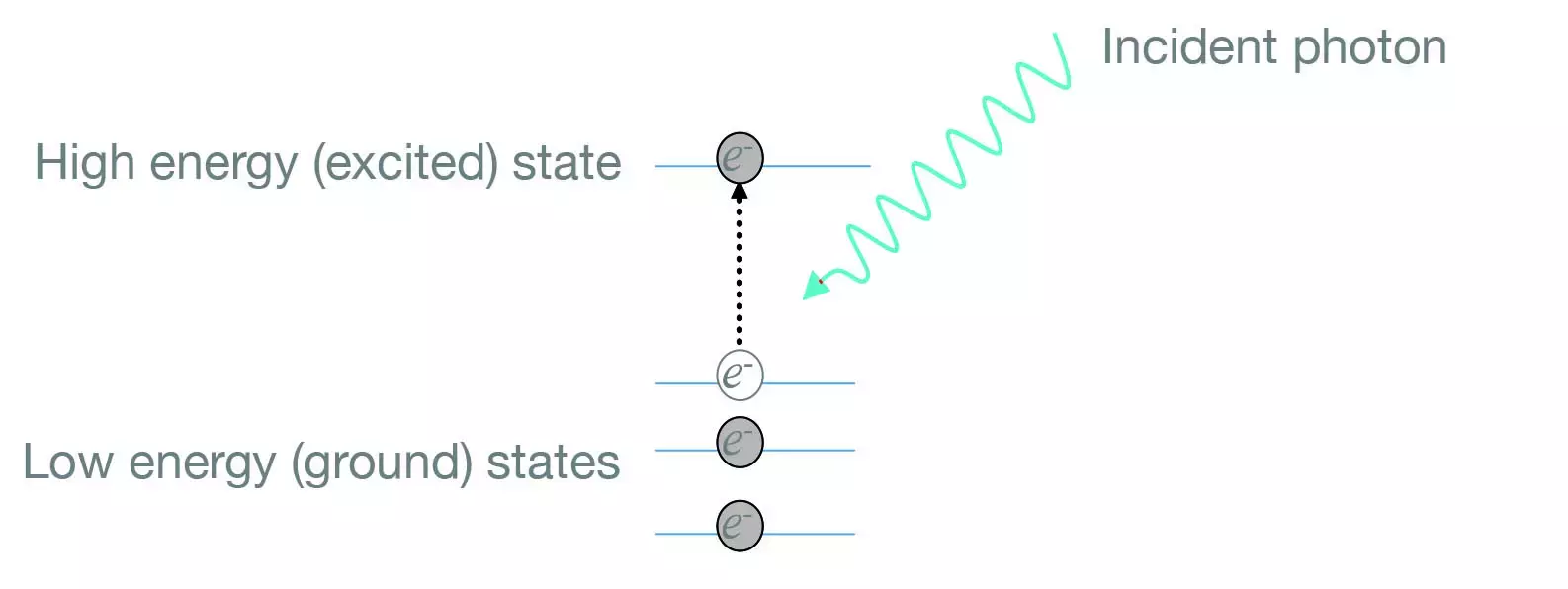
Excited State
When an atom or molecule absorbs energy the electrons are excited to move around more dynamically, referred to as an excited state. In an atom this is conceptually illustrated by imagining that the electrons move to orbits further away from the nucleus at the heart of the atom, though in effect the influence of the electron becomes more diffuse and extends further away from the nucleus.
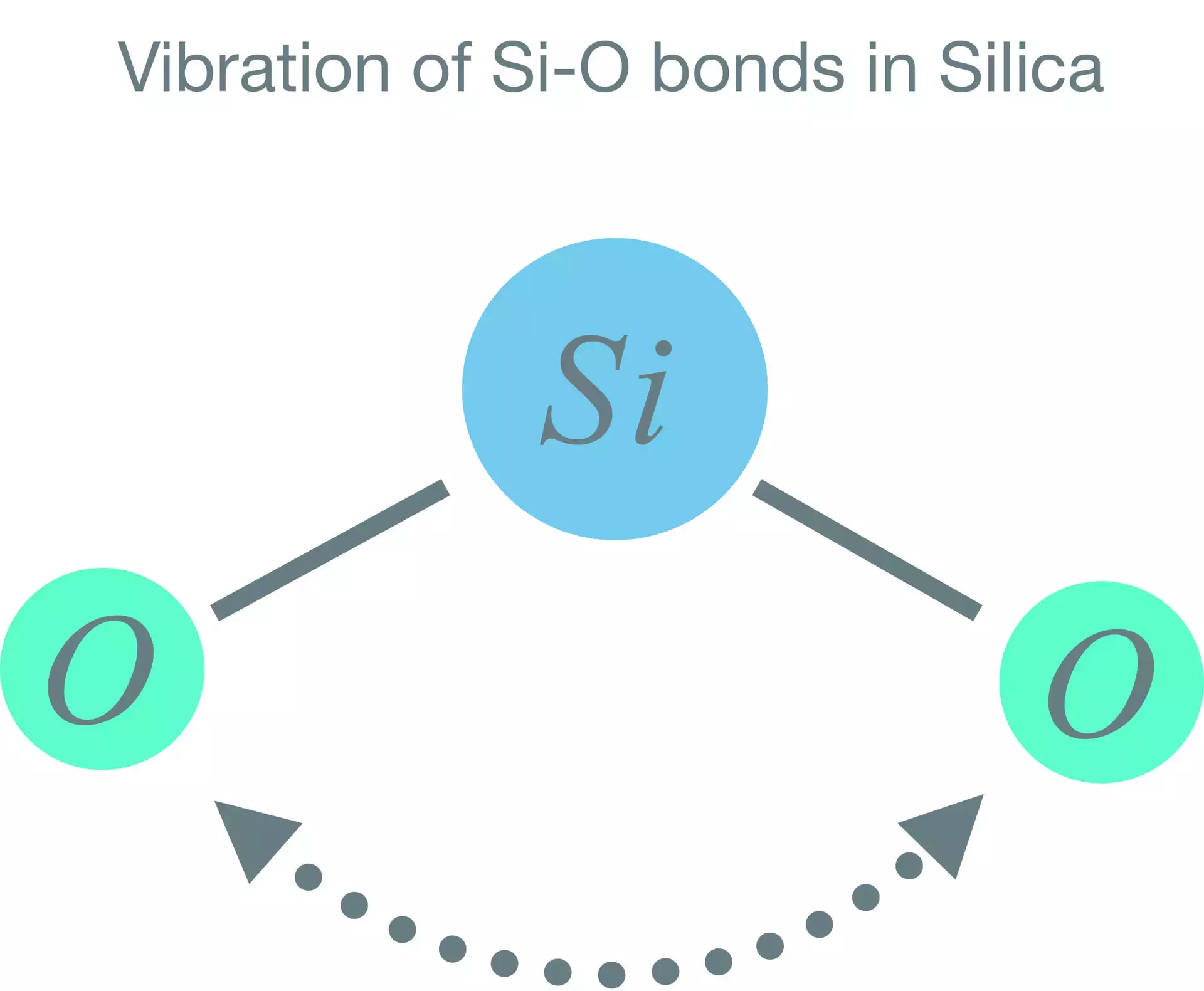
In a molecule the electrons moving between atoms forming bonds can encourage the relative orientation of the atoms to shift, making the molecule vibrate along its bonds. An example of this is the vibration of the Si-O bonds in the silica lattice of the glass in an optical fiber, which absorb energy in the infra-red causing molecular vibration.
Vibrational energy is transferred by phonons, which enable heat to propagate through a material and are involved in interactions between materials and light.
Related Products: Dual Clad Erbium/Ytterbium Doped Fiber, Erbium Doped Fiber IsoGain™, Erbium Doped Fiber MetroGain™, PM Erbium Doped Fiber, SM Erbium/Ytterbium Doped Fiber, SM Nd Doped Fiber, SM Ytterbium Doped Fiber
Related Terms: Absorption, Erbium, Excited State, Excited State Absorption (ESA), Irradiance, Light Emmitting Diode (LED)