Energy
Energy is often defined as the capacity of a system to do work. Outside of a physics lesson it is generally identified by its actions: it causes molecules to vibrate when it is manifest as temperature, electrons to move when it is manifest as electricity, and it causes us to see when it is manifest as light. Matter and energy have an equivalent defined by the well known equation.
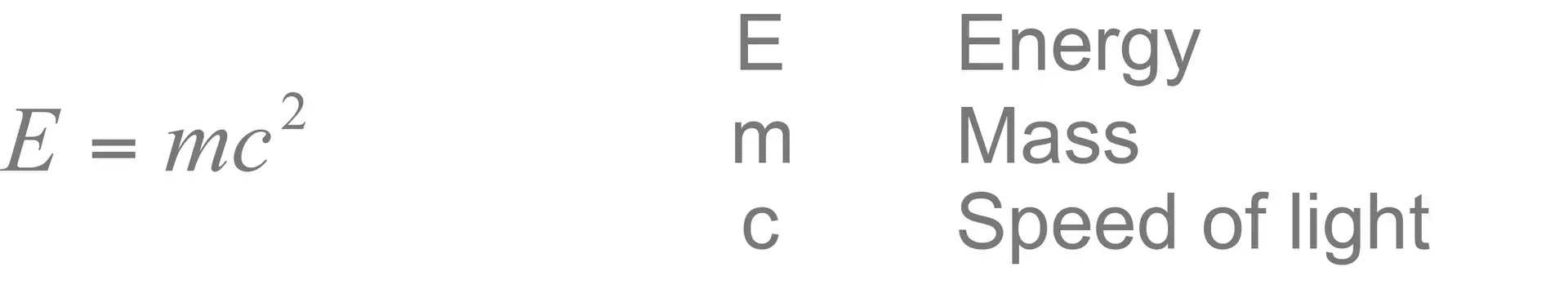
Similarly photons have an associated energy by virtue of their frequency. Frequency is unchanging in a photon or optical wave, though the wavelength will change depending on the medium, which gives rise to a variable phase velocity, even though the speed of light remains constant. The energy in a photon is defined by Plank’s constant:

The energy in a photon can be used with calculations related to the absorption and emission of an active fiber device, as well as power, photon density and quantum conversion efficiency.
Related Terms: Absorption, Emission Measurement, Emission Spectra, Excited State, Photon, Power, Quanta