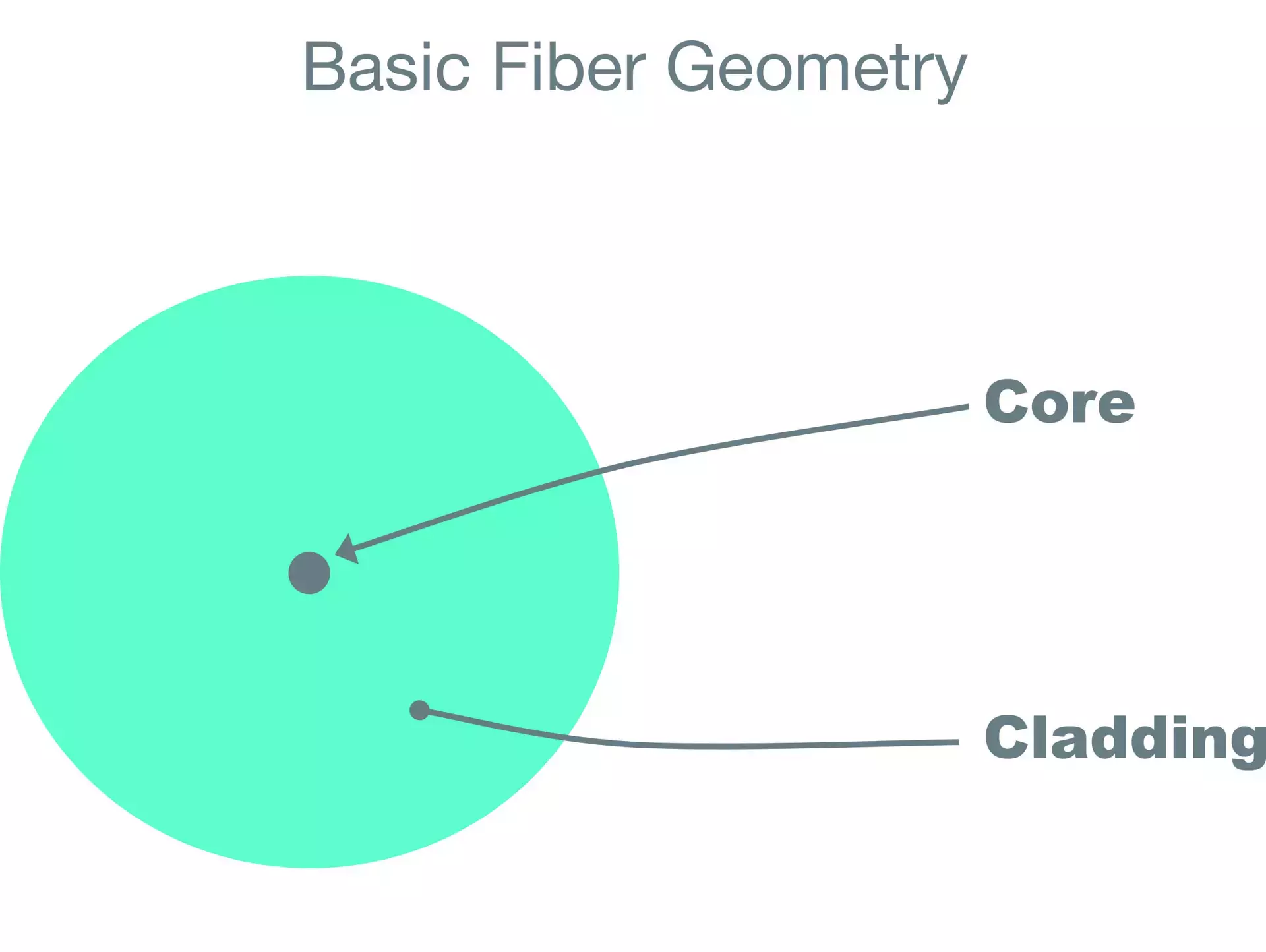
Core
The core is the central region of the optical fiber where the light is guided. In order to create guiding conditions, the refractive index of the core must be higher than the one of the cladding. The dimensions and composition of the core will have a direct impact on the optical properties and performance of an optical fiber.
For the majority of passive fibers in the market, the core is made of doped silica being Germania the most common and main dopant. For certain applications a pure silica core fiber is required, in which cases the cladding is often doped with Fluorine in order to reduce its refractive index allowing for guiding conditions. In active fibers, the core is generally doped with Germania as well as rare-earth materials to create an optical gain. In PMMA fibers both cladding and core would be made out of plastic materials of different refractive indexes.
Related Terms: Cladding, Core, Core Concentricity, Core Ellipticity, Refractive Index Profile (RIP), Silica, Waveguide